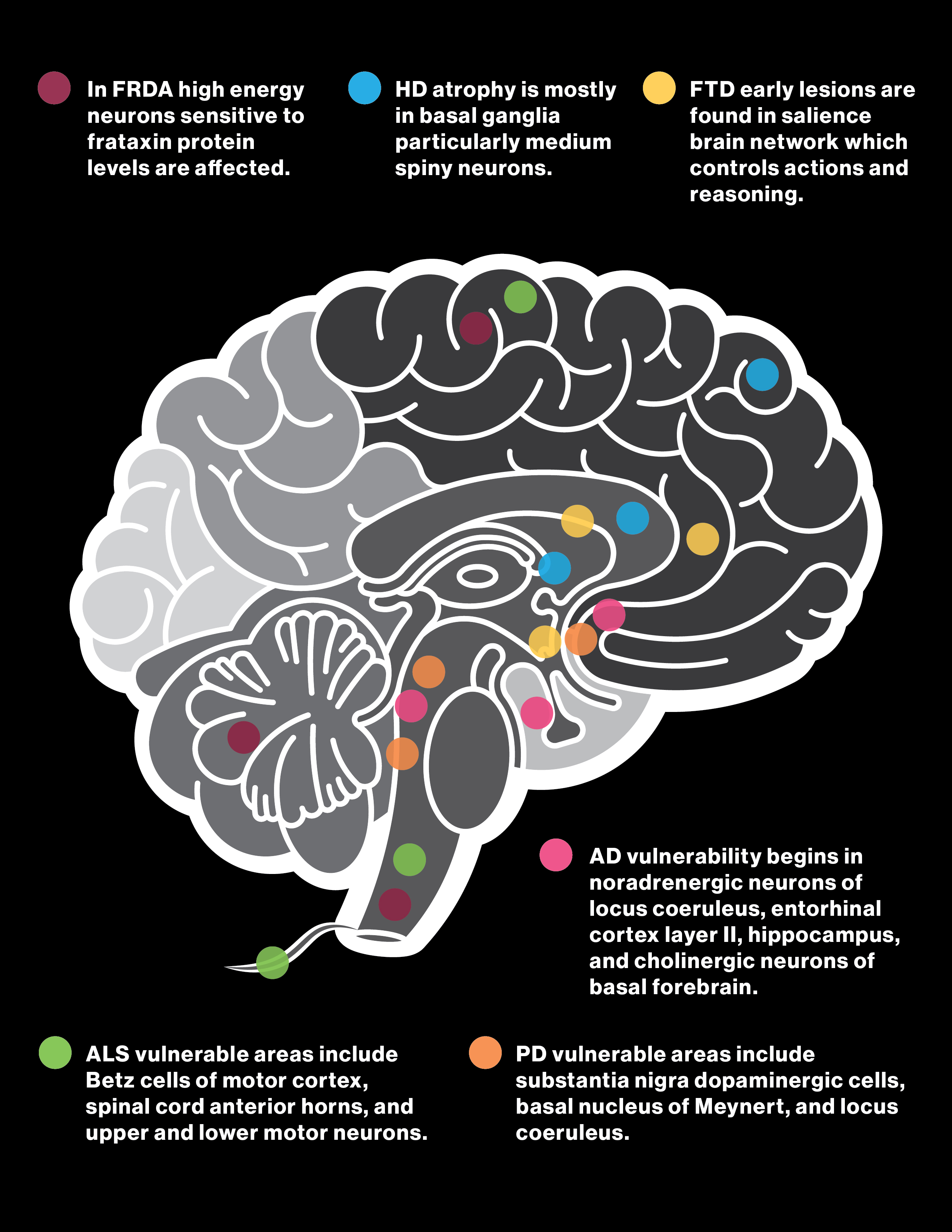
ATPL brain disease is a complex neurological condition that affects the brain's ability to produce and utilize ATP, an essential molecule for energy production. This condition has profound implications for both physical and cognitive health, making it crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of ATPL brain disease, providing a comprehensive guide for those seeking information about this condition.
ATPL brain disease is not just a medical term but a reality that impacts countless individuals globally. Understanding its underlying mechanisms can help in early detection and effective management. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, gaining insight into this condition can make a significant difference in managing its effects.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of ATPL brain disease, focusing on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how this condition affects the brain and what steps can be taken to manage it effectively.
Read also:Stone 248 A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Its Significance And Applications
Table of Contents
- Biography of ATPL Brain Disease
- Causes of ATPL Brain Disease
- Symptoms of ATPL Brain Disease
- Diagnosis of ATPL Brain Disease
- Treatment Options for ATPL Brain Disease
- Long-Term Management Strategies
- Current Research and Advancements
- Preventive Measures Against ATPL Brain Disease
- Support Systems for Patients and Families
- Conclusion
Biography of ATPL Brain Disease
ATPL brain disease refers to a group of neurological disorders that result from the disruption of ATP production in the brain. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary energy carrier in cells, and its deficiency can lead to severe functional impairments. Below is a summary of the key aspects of this condition:
Overview of ATPL Brain Disease
ATPL brain disease primarily affects the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell responsible for energy production. When ATP production is compromised, it leads to a cascade of effects that can impair cognitive function, motor skills, and overall brain health. This condition is often hereditary, but environmental factors can also play a role.
Data and Statistics
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), approximately 1 in 5,000 individuals may be affected by ATPL-related disorders. While the exact prevalence varies depending on the population, the condition is considered rare but highly impactful.
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence | 1 in 5,000 individuals |
| Age of Onset | Varies, but often manifests in early childhood |
| Genetic Component | Highly hereditary in most cases |
Causes of ATPL Brain Disease
The causes of ATPL brain disease are multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental components. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and management.
Genetic Factors
Mutations in genes responsible for mitochondrial function are the primary cause of ATPL brain disease. These mutations can impair the production of ATP, leading to energy deficits in brain cells. Common genetic mutations include those affecting the MT-ATP6 gene.
Environmental Triggers
While genetic predisposition is a significant factor, environmental triggers such as infections, toxins, and nutritional deficiencies can exacerbate the condition. For example, exposure to certain chemicals or a lack of essential nutrients like magnesium and B vitamins can worsen ATPL symptoms.
Read also:Exploring The Big Butler Fair A Celebration Of Community And Tradition
Symptoms of ATPL Brain Disease
The symptoms of ATPL brain disease can vary widely depending on the severity and progression of the condition. Early recognition of these symptoms is critical for timely intervention.
Neurological Symptoms
- Seizures
- Developmental delays
- Loss of motor skills
- Cognitive impairment
Physical Symptoms
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
- Heart problems
Diagnosis of ATPL Brain Disease
Diagnosing ATPL brain disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and imaging studies. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Clinical Evaluation
Healthcare providers assess the patient's medical history, family history, and current symptoms. This evaluation helps identify patterns indicative of ATPL-related disorders.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is a key component of diagnosing ATPL brain disease. It can identify specific mutations in genes associated with mitochondrial function, providing a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment Options for ATPL Brain Disease
While there is no cure for ATPL brain disease, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Medications
Medications such as anticonvulsants for seizure control and supplements like coenzyme Q10 and creatine can support ATP production and reduce symptoms.
Therapeutic Interventions
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help patients maintain and improve their functional abilities. These interventions are tailored to the individual needs of each patient.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Long-term management of ATPL brain disease requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare providers, caregivers, and support systems.
Regular Monitoring
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that treatment plans are adjusted as needed. Monitoring ATP levels and other biomarkers can help track disease progression.
Nutritional Support
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for supporting overall health and mitigating symptoms. Patients may benefit from working with a nutritionist to develop a personalized dietary plan.
Current Research and Advancements
Research into ATPL brain disease is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments and therapies. Advances in gene therapy and mitochondrial research offer hope for improved outcomes in the future.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy aims to correct the underlying genetic mutations causing ATPL brain disease. Clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this approach.
Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research holds promise for regenerating damaged brain cells and restoring ATP production. While still in the experimental phase, this field shows great potential for future treatments.
Preventive Measures Against ATPL Brain Disease
While prevention of ATPL brain disease is challenging due to its genetic nature, certain measures can reduce the risk of symptom exacerbation.
Genetic Counseling
For individuals with a family history of ATPL-related disorders, genetic counseling can help assess the risk of passing the condition to future generations.
Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding environmental toxins, can support overall brain health and reduce the impact of ATPL symptoms.
Support Systems for Patients and Families
Living with ATPL brain disease can be challenging, but support systems are available to help patients and families navigate the complexities of this condition.
Support Groups
Joining a support group can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community for those affected by ATPL brain disease.
Professional Counseling
Counseling services can help patients and families cope with the psychological and emotional aspects of living with a chronic illness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ATPL brain disease is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, patients and families can effectively manage this condition and improve their quality of life.
We encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from its insights. For more information on ATPL brain disease and related topics, explore our other articles and resources. Together, we can raise awareness and support those affected by this condition.