Weather tornadoes are among the most destructive and unpredictable natural phenomena on Earth. These powerful storms can wreak havoc in a matter of seconds, causing significant damage to property and posing serious threats to human life. Understanding the science behind tornadoes and how to prepare for them is crucial for anyone living in tornado-prone areas.
Tornadoes are not just random acts of nature; they follow specific patterns and behaviors that scientists have been studying for decades. By learning about the causes, characteristics, and warning signs of tornadoes, individuals can better protect themselves and their loved ones during severe weather events.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of weather tornadoes, including their formation, impact, and safety measures. Whether you're a weather enthusiast or someone who wants to stay safe during a tornado, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate these powerful storms.
Read also:Exploring The Fusion Of Umami Sauce Kimono And Mom Culture
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Weather Tornadoes
- What Are Tornadoes?
- How Do Tornadoes Form?
- Tornado Classification and Strength
- Tornado Alleys and High-Risk Areas
- The Impact of Weather Tornadoes
- Tornado Safety Tips
- Warning Signs of an Approaching Tornado
- Technology in Tornado Prediction
- Conclusion
Introduction to Weather Tornadoes
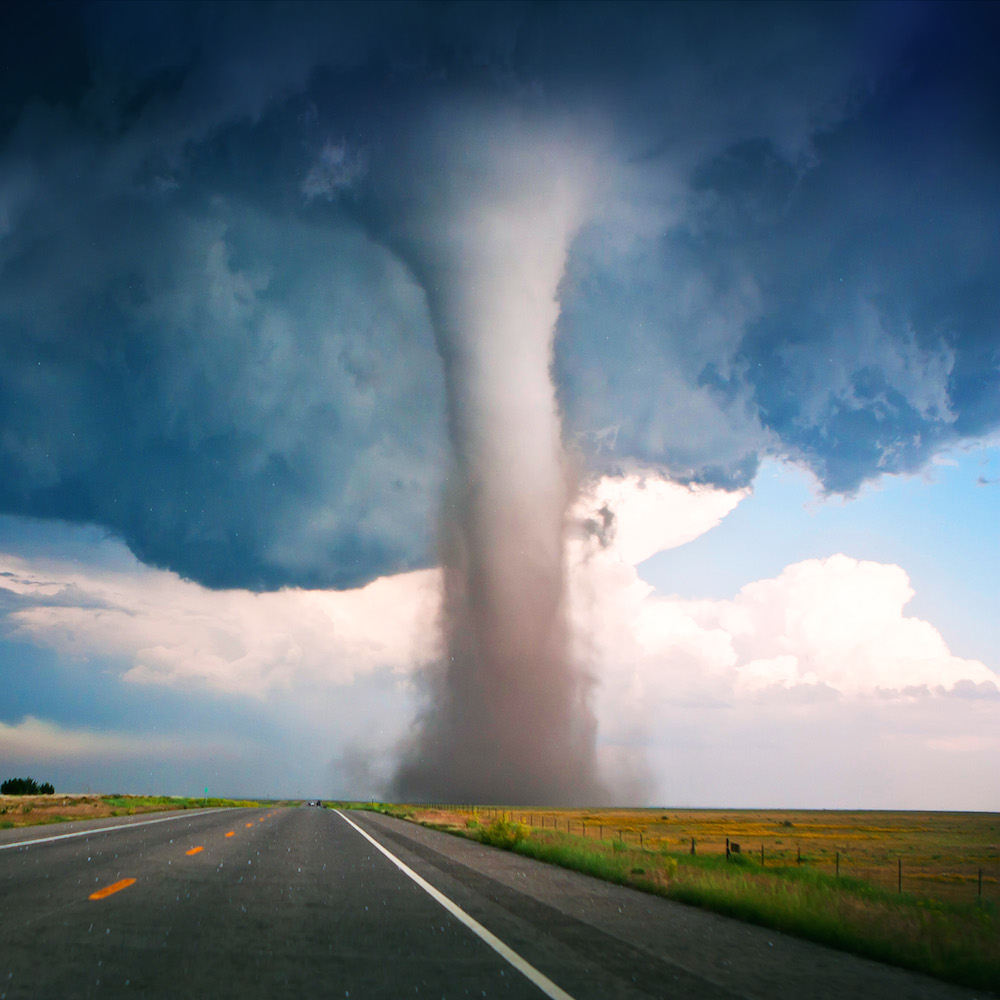
Weather tornadoes are violent rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground. These storms are capable of producing winds exceeding 300 miles per hour, making them one of the most dangerous weather events on the planet. Understanding the basics of tornadoes is the first step in preparing for their potential impact.
What Are Tornadoes?
Tornadoes are essentially nature's most violent storms, characterized by their funnel-shaped clouds and intense wind speeds. They occur when warm, moist air collides with cool, dry air, creating an unstable atmosphere. This instability can lead to the formation of supercell thunderstorms, which are the primary producers of tornadoes.
Key Characteristics:
- Tornadoes can vary in size, from a few yards to over a mile wide.
- They typically last between a few minutes to an hour, but some have been known to last longer.
- The Fujita Scale is used to measure the intensity of tornadoes based on wind speed and damage.
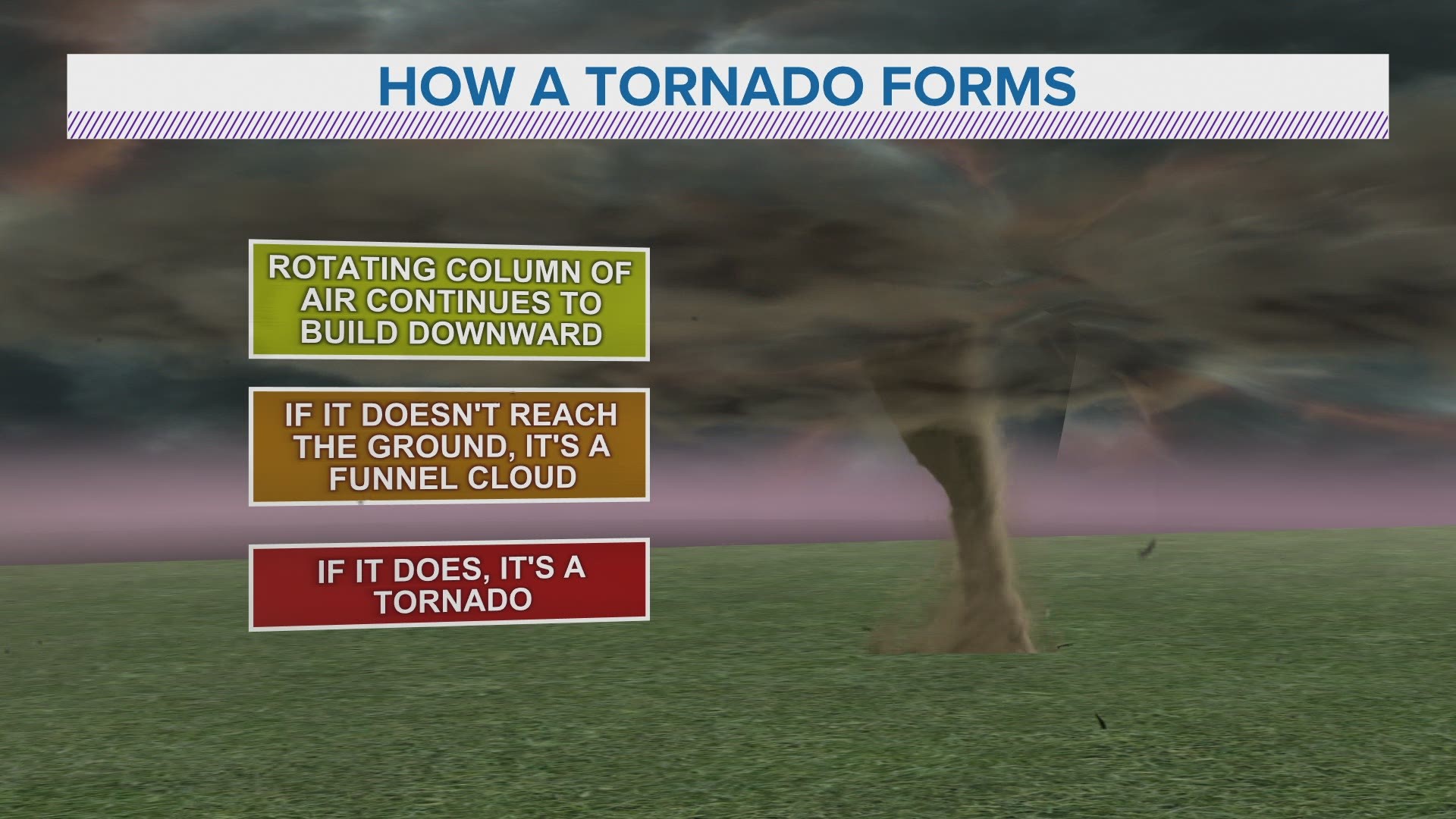
How Do Tornadoes Form?
The formation of a tornado involves a complex interaction of atmospheric conditions. It begins with the development of a supercell thunderstorm, which is a type of storm characterized by a persistent rotating updraft known as a mesocyclone. When this rotation extends from the cloud base to the ground, a tornado is born.
Key Factors in Tornado Formation
- Wind Shear: A change in wind speed and direction with height creates the rotation necessary for tornado development.
- Instability: Warm, moist air near the surface rises, meeting cooler air aloft, creating the energy needed for a storm.
- Lift: Fronts, drylines, or other weather features provide the lift needed to trigger the storm.
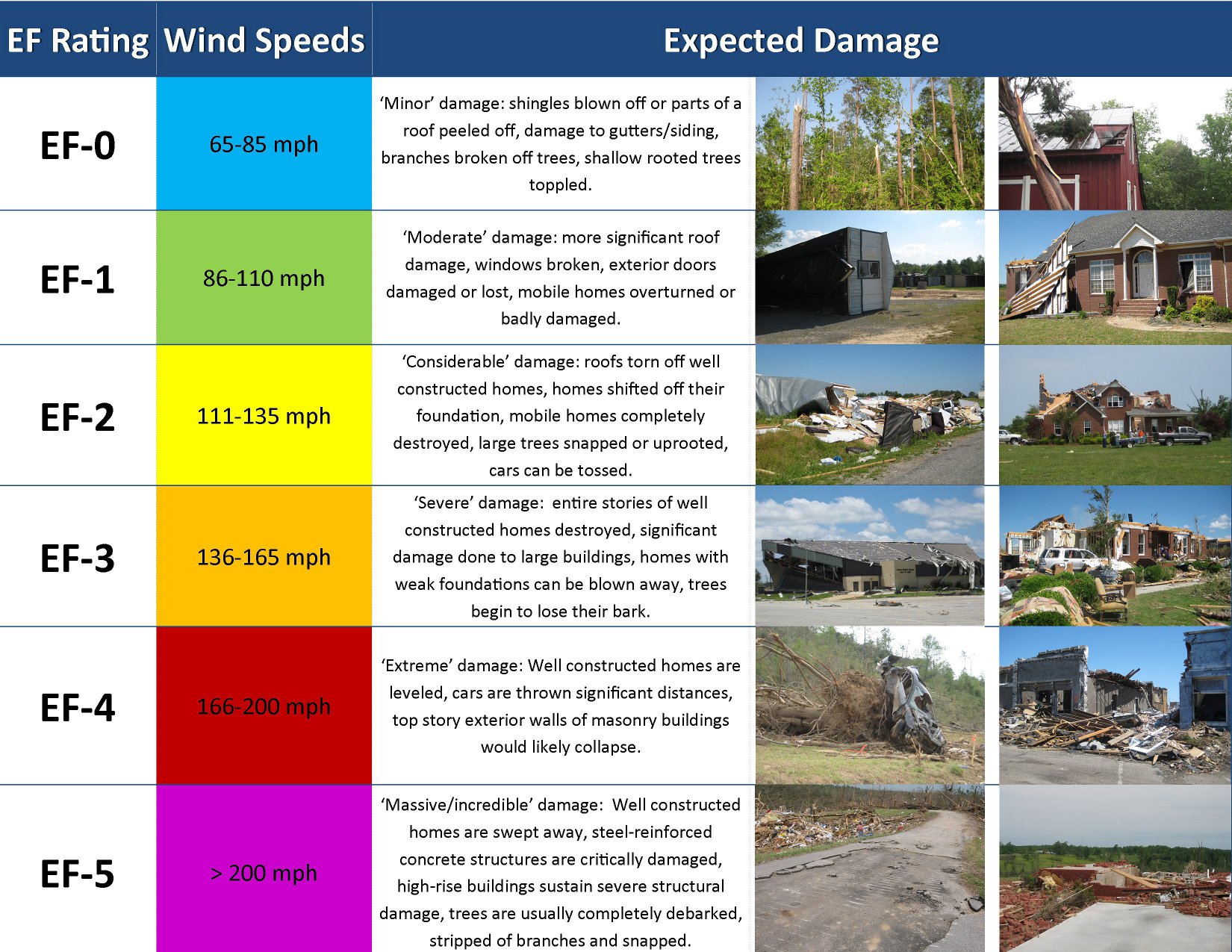
Tornado Classification and Strength
Tornadoes are classified based on their wind speed and the damage they cause. The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale is the most widely used system for categorizing tornadoes. It ranges from EF0 (weakest) to EF5 (strongest).
EF Scale Breakdown:
Read also:How Tall Is Jojo Siwa Everything You Need To Know About Her Height And More
- EF0: 65-85 mph winds, minor damage to structures.
- EF1: 86-110 mph winds, moderate damage to homes and trees.
- EF2: 111-135 mph winds, significant damage to roofs and mobile homes.
- EF3: 136-165 mph winds, severe damage to well-constructed homes.
- EF4: 166-200 mph winds, devastating damage, leveling entire homes.
- EF5: Over 200 mph winds, catastrophic destruction, with homes completely swept away.
Tornado Alleys and High-Risk Areas
Tornadoes are more common in certain regions of the world, with the United States being home to the infamous "Tornado Alley." This area, stretching from Texas through Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska, experiences the highest frequency of tornadoes due to its unique geography and climate.
Global Tornado Hotspots
- United States: Tornado Alley is the most famous tornado-prone region globally.
- Canada: Southern Alberta and Saskatchewan also see frequent tornado activity.
- Europe: Countries like the United Kingdom and Italy experience tornadoes, though less intense than those in the U.S.
The Impact of Weather Tornadoes
The impact of tornadoes extends beyond just physical destruction. They can cause emotional trauma, economic losses, and long-term disruptions to communities. Understanding the full scope of their effects is essential for effective disaster response and recovery.
Economic and Social Consequences
- Property Damage: Tornadoes can destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure, leading to billions in economic losses annually.
- Human Costs: Injuries and fatalities are common during severe tornado outbreaks, highlighting the importance of preparedness.
- Community Recovery: Rebuilding after a tornado can take years, requiring significant resources and support.
Tornado Safety Tips
Staying safe during a tornado requires preparation and quick thinking. Here are some essential tips to help you and your family survive a tornado:
Before a Tornado
- Create an emergency plan and practice tornado drills with your family.
- Assemble a disaster supply kit with essentials like water, food, and first aid supplies.
- Identify safe rooms or shelters in your home or community.
During a Tornado
- Seek shelter immediately in a basement or interior room on the lowest level of a building.
- Stay away from windows and exterior walls to avoid flying debris.
- Protect your head and neck with a helmet or cushion.
Warning Signs of an Approaching Tornado
Recognizing the warning signs of a tornado can save lives. Look out for the following indicators:
- Dark, Often Greenish Sky: A greenish hue in the sky can indicate a severe storm.
- Loud Roaring Sound: Similar to a freight train, this noise is often heard during a tornado.
- Debris in the Air: Flying debris is a clear sign of a tornado's presence.
Technology in Tornado Prediction
Advancements in technology have significantly improved tornado prediction and warning systems. Doppler radar, satellite imagery, and computer models allow meteorologists to track storms in real-time and issue warnings with greater accuracy.
Future Developments
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are being used to analyze vast amounts of weather data to improve forecasting.
- Drone Technology: Drones are being deployed to study tornadoes up close, providing valuable insights into their behavior.
Conclusion
Weather tornadoes are powerful and unpredictable forces of nature that require respect and preparation. By understanding their formation, classification, and impact, individuals can take the necessary steps to protect themselves and their communities. Remember to stay informed, follow safety guidelines, and utilize modern technology to stay ahead of these storms.
We invite you to share this article with others and leave your thoughts in the comments below. For more information on weather safety and preparedness, explore our other articles on this site. Stay safe and informed!
References:
- NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory
- Weather Channel
- World Meteorological Organization