The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a pivotal role in the United States' monetary policy decisions, making it an essential entity to understand for anyone interested in economics, finance, or investing. This powerful committee is responsible for setting key interest rates and conducting open market operations, both of which significantly influence the nation's economy. By examining its structure, functions, and decision-making processes, we can gain valuable insights into how it shapes economic outcomes.
As one of the most influential economic bodies globally, the FOMC has far-reaching implications not only for the U.S. but also for the global financial markets. Its decisions affect everything from mortgage rates and credit card interest to the broader stock and bond markets. Understanding its operations can help individuals make informed financial decisions, whether they're investors, businesses, or everyday consumers.
This article will delve into the intricacies of the FOMC, exploring its history, responsibilities, and the impact of its policies on the economy. We'll also examine how it operates, its key players, and the tools it employs to manage monetary policy. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a novice in the world of finance, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the FOMC and its role in shaping economic policy.
Read also:Rpm Italian Washington Dc A Culinary Experience Like No Other
Table of Contents
- Introduction to FOMC
- History of the FOMC
- Structure of the FOMC
- Responsibilities and Functions
- FOMC Meetings and Decision-Making
- Monetary Policy Tools
- Impact on the Economy
- Global Influence of FOMC Decisions
- Criticisms and Challenges
- Future of the FOMC
Introduction to FOMC
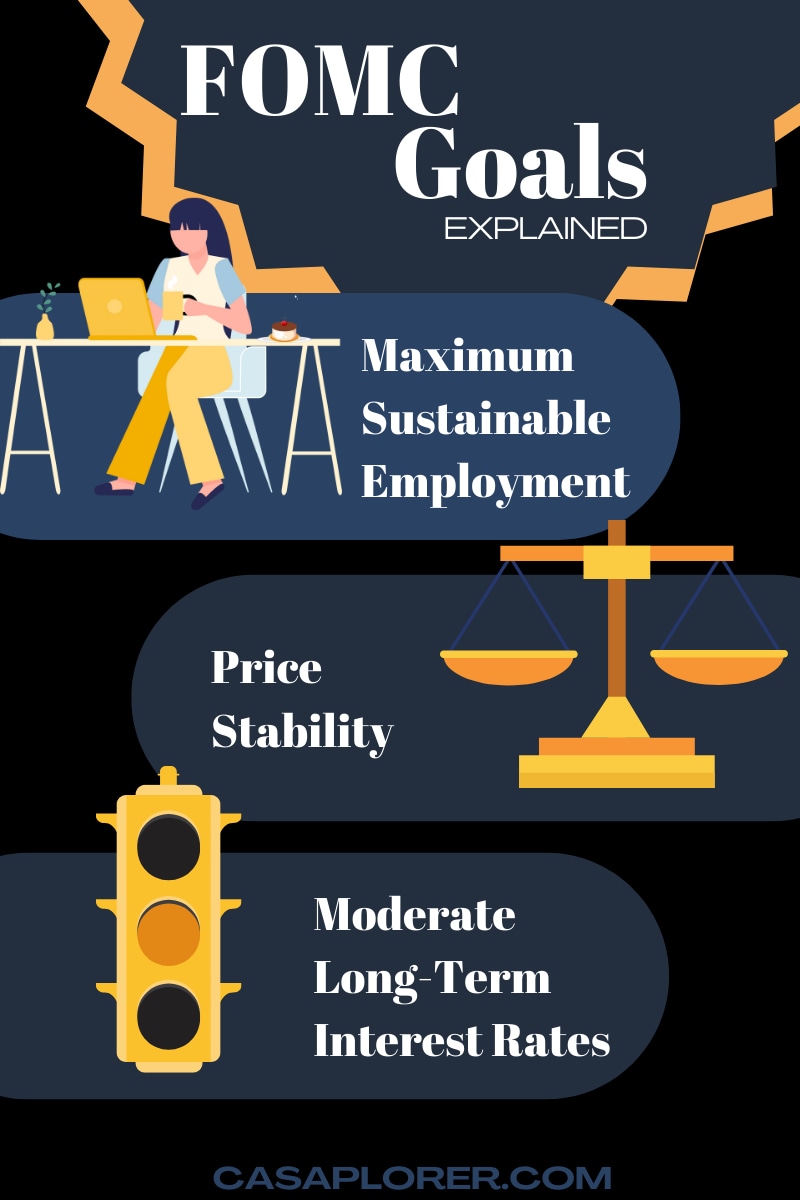
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a crucial component of the Federal Reserve System, often referred to as the Fed. Established in 1913 under the Federal Reserve Act, the FOMC is tasked with implementing monetary policy in the United States. Its primary objective is to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
Operating independently within the government, the FOMC makes decisions regarding interest rates and the money supply. By buying and selling government securities, the committee influences the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to other banks overnight.
Understanding the FOMC’s role is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the broader economic landscape. Its decisions ripple through the economy, affecting everything from personal savings to corporate investments.
History of the FOMC
Origins and Evolution
The FOMC's origins trace back to the Banking Act of 1935, which restructured the Federal Reserve System to centralize monetary policy decisions. Initially, the FOMC consisted of the seven members of the Board of Governors and five Reserve Bank presidents. Over the years, the committee's structure and responsibilities have evolved to meet the changing needs of the economy.
In response to the Great Depression, the FOMC began to play a more active role in stabilizing the economy. Its mandate expanded to include promoting economic growth and reducing unemployment, alongside maintaining price stability.
Milestones in FOMC History
- 1970s Inflation Crisis: The FOMC faced significant challenges during the high inflation period, implementing aggressive monetary tightening to control rising prices.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: The committee introduced unprecedented measures, including quantitative easing, to stabilize the financial system and stimulate economic recovery.
Structure of the FOMC
Composition and Membership
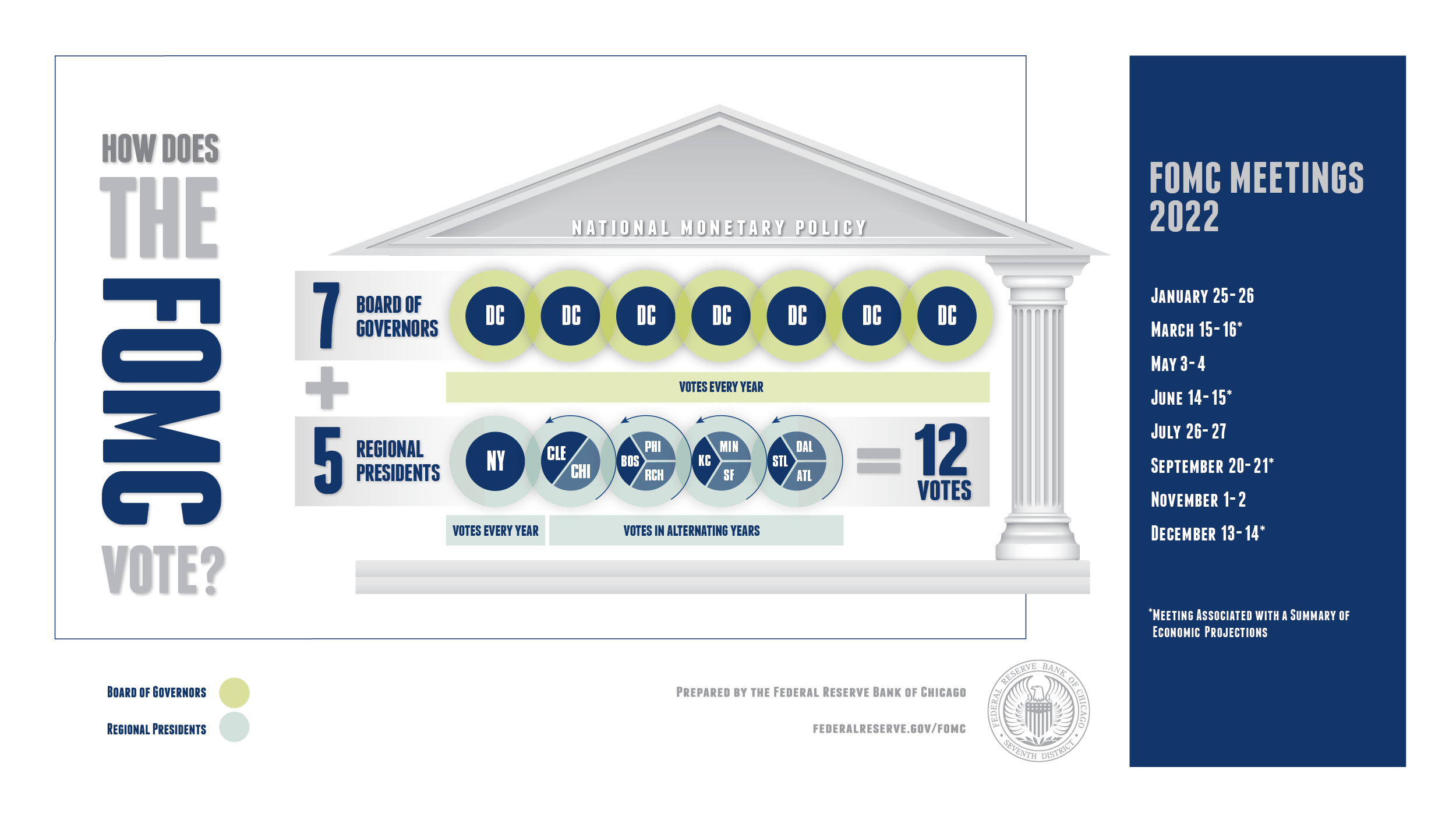
The FOMC comprises twelve members: seven members of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and five of the twelve Reserve Bank presidents. The president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York serves as a permanent voting member, while the remaining four positions rotate annually among the other Reserve Bank presidents.
Read also:Lizard From Monsters Inc With Glasses A Deep Dive Into This Iconic Character
This structure ensures a balance between centralized oversight and regional perspectives, allowing the committee to make informed decisions that reflect the diverse economic conditions across the nation.
Roles and Responsibilities of Members
Each member brings unique expertise and insights to the table. The Board of Governors provides a national perspective, while the Reserve Bank presidents offer regional economic intelligence. This collaborative approach strengthens the FOMC's ability to formulate effective monetary policy.
Responsibilities and Functions
Setting Monetary Policy
The FOMC's primary responsibility is to set monetary policy to achieve its dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability. It does this by adjusting the federal funds rate, which influences borrowing costs throughout the economy.
Conducting Open Market Operations
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government securities to influence the money supply and credit conditions. By altering the availability of funds in the banking system, the FOMC can stimulate or slow economic activity.
FOMC Meetings and Decision-Making
Schedule and Frequency
The FOMC holds eight regularly scheduled meetings per year, with additional meetings called as needed. During these meetings, members review economic and financial conditions, assess risks to the outlook, and determine appropriate monetary policy actions.
Decision-Making Process
Decisions are made by a majority vote, with each member casting one vote. The committee considers a wide range of economic indicators, including employment data, inflation rates, and GDP growth, to inform its decisions.
Monetary Policy Tools
Interest Rate Adjustments
One of the FOMC's most powerful tools is its ability to adjust the federal funds rate. By raising or lowering this rate, the committee can influence borrowing costs and, consequently, economic activity.
Quantitative Easing and Tightening
During periods of economic distress, the FOMC may engage in quantitative easing, purchasing large quantities of government securities to inject liquidity into the economy. Conversely, quantitative tightening involves reducing the central bank's balance sheet to remove excess liquidity.
Impact on the Economy
Effects on Employment and Inflation
The FOMC's policies directly impact employment levels and inflation rates. By maintaining low and stable inflation, the committee helps preserve the purchasing power of consumers and businesses. Its efforts to promote maximum employment contribute to a robust labor market.
Influence on Financial Markets
FOMC decisions have a profound effect on financial markets. Changes in interest rates can lead to shifts in stock and bond prices, affecting investor sentiment and portfolio allocations.
Global Influence of FOMC Decisions
Impact on International Markets
The FOMC's actions resonate globally, influencing currency exchange rates, trade balances, and capital flows. As the world's largest economy, the U.S. monetary policy decisions have significant spillover effects on other nations.
Coordination with Global Central Banks
The FOMC often collaborates with other central banks to address global economic challenges. Such coordination can help stabilize international financial markets and promote global economic growth.
Criticisms and Challenges
Political Pressure
Despite its independence, the FOMC occasionally faces political pressure to adopt policies that align with short-term political goals rather than long-term economic stability. This can undermine its credibility and effectiveness.
Economic Uncertainty
Unforeseen economic shocks, such as pandemics or geopolitical conflicts, pose significant challenges to the FOMC's ability to predict and respond to economic conditions effectively.
Future of the FOMC
Adapting to New Economic Realities
As the economy evolves, the FOMC must continually adapt its strategies and tools to address emerging challenges. This includes incorporating new technologies, data analytics, and economic models into its decision-making processes.
Innovations in Monetary Policy
Looking ahead, the FOMC may explore innovative approaches to monetary policy, such as average inflation targeting and digital currencies, to enhance its ability to achieve its mandates in a rapidly changing economic landscape.
Conclusion
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a critical role in shaping the economic environment through its monetary policy decisions. By understanding its structure, responsibilities, and tools, individuals and businesses can better navigate the financial landscape and make informed decisions.
We encourage readers to engage with this content by leaving comments or questions below. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from understanding the FOMC's impact on the economy. For more insights into financial topics, explore our other articles and resources.
Data and references for this article were sourced from the Federal Reserve Board, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, and other reputable financial institutions. This ensures the information provided is accurate and up-to-date.